Whenever someone reports some weird error on my blog comments or sends email to know about it, I always ask to share SQL Server ERRORLOG file. There have been many occasions where I need to guide them to find location of ERRORLOG file generated by SQL Server. Most DBA’s are intelligent and know some of these, but this is my try to share my learning about ERRORLOG location.
I decided to write this blog so that I can reuse it rather than sending steps every time. At this point I must point out that even if the name says ERRORLOG, it contains not only the errors but information message also. Here are various ways to find the SQL Server ErrorLog location.
A) If SQL Server is running and we are able to connect to SQL Server then we can do various things. So we can connect to SQL Server and run xp_readerrorlog.
USE MASTER GO EXEC xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N'Logging SQL Server messages in file' GO
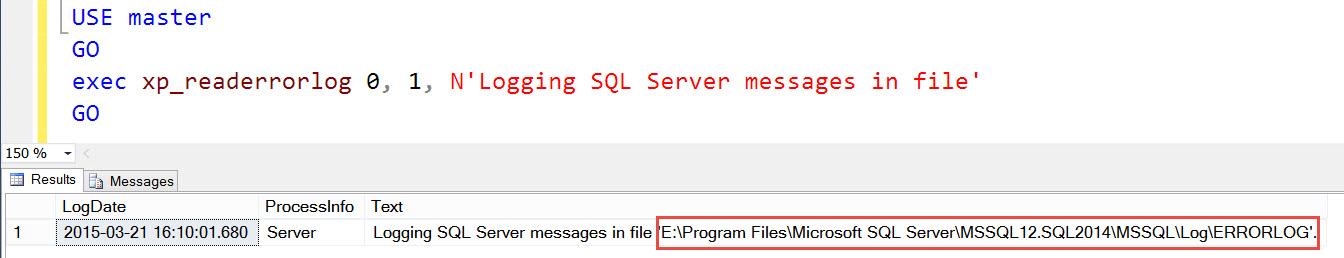
If you can’t remember above command just run xp_readerrorlog and find the line which says “Logging SQL Server messages”.
B) If we are not able to connect to SQL Server then we should SQL Server Configuration Manager use. We need to find startup parameter starting with -e. Below is the place in SQL Server Configuration Manager (SQL 2012 onwards) where we can see them.

C) If you don’t want to use both ways, then here is the little unknown secret. The ERRORLOG is one of startup parameters and its values are stored in registry key and here is the key in my server. SQLArg1 shows parameter starting with -e parameters which point to Errorlog file.

Here is the key which I highlighted in the image: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL12.SQL2014\MSSQLServer\Parameters\
Note that “MSSQL12.SQL2014” would vary based on SQL Server Version and instance name which is installed. Here is the quick table with version reference
| SQL Server Version | Key Name |
| SQL Server 2008 | MSSQL10 |
| SQL Server 2008 R2 | MSSQL10_50 |
| SQL Server 2012 | MSSQL11 |
| SQL Server 2014 | MSSQL12 |
In SQL Server 2005, we would see a key name in the format of MSSQL.n (like MSSQL.1) the number n would vary based on instance ID.
Here is a key where we can get mapping of Instance ID and directory.
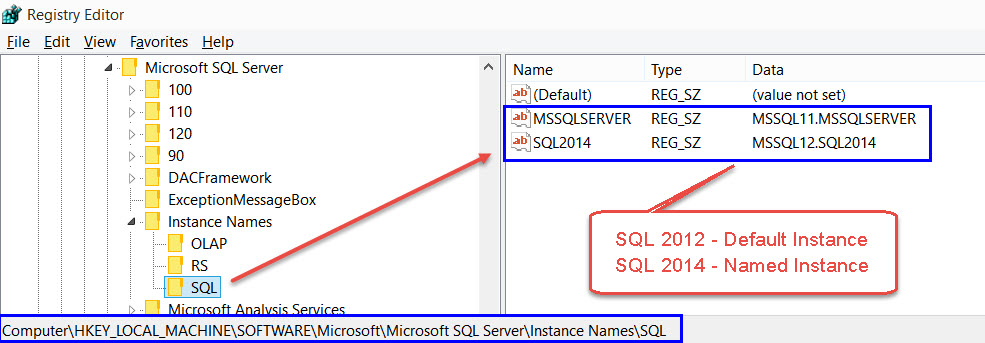
In the above image, you can see that this computer has a default instance (Instance Name MSSQLSERVER) of SQL Server 2012 and named instance (Instance Name SQL2014) of SQL Server 2014.
In case you are contacting me for any error, get the Errorlog location using this blog.
Reference: Pinal Dave (https://darkslategrey-bat-805937.hostingersite.com)